Nessus Crack v8.1.1 is brought into any conversation. So, almost no one thinks about a computer program. So, almost no one thinks about a computer program. Hence, let alone a specific application software that audits networks.
When it comes to network security, most of the tools to test your network are pretty complex. Nessus isn’t new, but it definitely bucks this trend. It’s incredibly easy to use, works quickly, and can give you a quick rundown of your network’s security at the click of a button.
How to Hack Your Own Network and Beef Up Its Security with Kali Linux
Kali Linux is a security-focused operating system you can run off a CD or USB drive, anywhere. With …
Read more ReadAdvertisement
- Hacking Tutorial 07 - Vulnerability Scanning with Nessus (Part 1 - Setting Up Nessus) Tech Ruse. Introduction to Vulnerability Assessment with Nessus - Duration: 24:15.
- Attackers first target is to crack windows user names and passwords on a organization network and then escalate privileges to Domain admin account. What tools do you use for Network Penetration testing? Kali linux has many open source penetration testing tools. Port Scanners: Nmap; Network Vulnerability Scanners: Nessus, Nexpose.
This post is part of our Evil Week series at Lifehacker, where we look at the dark side of getting things done. Sometimes evil is justified, and other times, knowing evil means knowing how to beat it. Want more? Check out our evil week tag page.
Welcome to Lifehacker's Seventh Annual Evil Week
It’s that time of year again: As Halloween approaches, it’s time to unleash our dark side. Welcome…
Read more ReadAdvertisement
If someone wanted to hack your local network, the first thing they’d do is run a vulnerability scan, then they’d run a penetration test. A vulnerability scan digs through the various devices on your network and looks for potential holes, like open ports, outdated software with known vulnerabilities, or default passwords on devices. If they find anything, a hacker would test those vulnerabilities, then find a way to exploit them. Testing these vulnerabilities is a two-step process because a scan just reveals the possibility of problems, a penetration test verifies that the problem is actually exploitable.
Nessus is commercial software made to scan for vulnerabilities, but the free home version offers plenty of tools to help explore and shore up your home network. It also point you to a variety of different tools to then penetration test a network if you want to learn more. Here’s how to use it.
Advertisement
Step One: Download and Install Nessus
Advertisement
In order to download Nessus, you’ll first need to sign up for an online account so you can download the software and get an activation code.
- Head to the Nessus Home landing page, enter a name and email address, and then click the Register button. You’ll want to use a real email address here because Nessus sends you an activation code that you’ll need in a step later.
- Click the Download button, then download Nessus for your operating system. It’s available for Windows, Mac, and Linux.
- Once the download is complete, run the installer package and follow the on-screen instructions to finish installation.
Advertisement
Nessus creates a local server on your computer and runs from there, so don’t be surprised that the installation process is a little different than you’re used to.
Step Two: Set Up Your Nessus Account and Activation Code
Once Nessus is installed, point your web browser to: https://localhost:8834/ This is where we’ll complete the signup process and activate your copy of Nessus.
Nessus Vulnerability Scanner Crack Download
Advertisement
- When you launch Nessus for the first time, you get a “Your connection is not secure” warning from your browser. Click “Advanced” and then “Proceed to localhost” to bypass this warning.
- Create an account on the Account Setup screen, leave the Registration as “Home, Professional, or Manager,” and then enter the Activation Code from your email. Click “Continue.”
Advertisement
Next, Nessus will download a number of tools and plugins so it can properly scan your network with updated utilities. This can take a few minutes, so grab a cup of coffee and make yourself comfortable.
Step Three: Start a Vulnerability Scan
Advertisement
It’s time to actually test your network. This is the fun part. Nessus can actually scan for quite a few different problems, but most of us will be content using the Basic Network Scan because it offers a good overview.
- Click the “New Scan.”
- Click “Basic Network Scan.”
- Name your scan and add a description.
- In the “Targets” field, you’ll want to enter IP scanning details about your home network. For example, if your router is at 192.168.0.1, you’d want to enter
192.168.0.1/24. This will make it so Nessus scans all the devices on your network (unless you have a ton of devices this is probably as high as you’d need to go). If you’re not sure about the local IP address for your router, here’s how to find it. - Click “Save.”
- On the next screen, click the Play icon to launch the scan.
Depending on what and how many devices you have on your network, the scan takes a while, so sit back and relax while Nessus does its work.
Advertisement
Aside from the Basic Network Scan, you can also run an Advanced Scan that includes more parameters to narrow your search, a Badlock Detection scan, which hunts down a security issue with SAMBA, a Shellshock scan that looks for vulnerabilities in old Linux or Mac machines, a DROWN scan that looks for computers hosting sites susceptible to DROWN attacks, and a few other more acute scans. Most of these issues will also get picked up with the Basic Network Scan, but if you’re doing anything beyond just maintaining a normal home network, like running a private server that’s exposed to the Internet, then you’ll want to double-check that everything is up-to-date using the more specific scanning modes. The rest of us will be fine with the Basic Network Scan.
Step Four: Make Sense of the Results
Advertisement
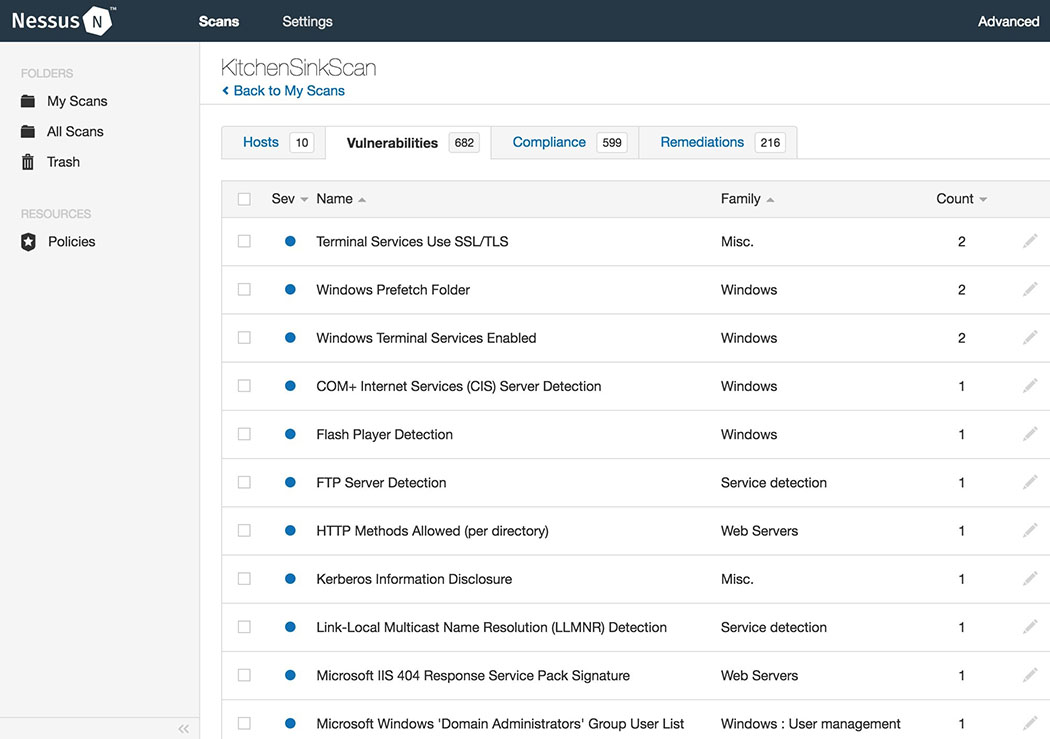
Once Nessus finishes, you’ll see a bunch of color-coded graphs for each device (referred to as hosts) on your network. Each color of the graph signifies the danger of a vulnerability, from low to critical.
Your results should include all the devices on your local network, from your router to your Wi-Fi-enabled printer. Click the graph to reveal more information about the vulnerabilities on each device. Vulnerabilities are listed as “plugins,” which is just Nessus’ way of discovering vulnerabilities. Click on any plugin to get more information about the vulnerability, including white papers, press releases, or patch notes for potential fixes. You can also click the Vulnerabilities tab to see an overview of all the potential vulnerabilities on the network as a whole.
Advertisement
Take a second to click the link on each vulnerability, then read up on how a hacker could exploit it. For example, I have an old Apple TV with an ancient firmware installed because it’s never used. Nessus found it and marked it as a “High” priority vulnerability, then links to Apple’s own security update page for more information. This lets me know that a hacker can exploit the Apple TV’s firmware by setting up a fake access point. The vulnerability page also helpfully lists exactly what software one would need to penetration test and hack that vulnerability. For example, Nessus lists Metasploit as the toolkit needed to exploit this weak point and with that knowledge, you can search Google for instructions on how to take advantage of the vulnerability.
There’s a chance some of these vulnerabilities will be a bit obvious. For example, Nessus picks up on any device still using a default password or points out when a computer or device is running an outdated firmware. Most of the time though, you probably won’t understand what the heck you’re looking at with these results.
Advertisement
Step Five: What to Do Next
Advertisement
Nessus gives you all this data, but what exactly are you supposed to do with it? That depends on which vulnerabilities Nessus finds.
After your scan is complete, click the Remediations tab. Here, you’ll find the biggest potential security holes in your network. In my case, alongside that Apple TV, this includes an ancient version of Adobe AIR installed on my laptop, an old version of Firefox, a Raspberry Pi running an old version of Apache, and a few others. All of these issues are easily remedied by either updating or deleting old software. You might think you’re vigilant about updating your software, but so do I, and yet I still had plenty of weird old software I never use sitting around creating potential access points for a hacker. You mileage will of course vary here, but regardless of your results, Nessus provides the information you need to close any holes.
Advertisement
While all this might sound a little scary, it’s worth noting that while Nessus gives you a lot of the potential ways into a network, it’s not a foolproof guide. On top of needing to be in your network in the first place (which of course, isn’t terribly complicated), they’d also need to know how to actually use the variety of the exploitation tools Nessus suggests.
While the exploit on my Apple TV could potentially grant someone access to the device, that doesn’t necessarily mean they’d be able to do anything once they’re there. Regardless, as an end-user who’s simply trying to shore up a network, Nessus is a great starting point for finding the most obvious vulnerabilities that could make you an easy target, or to just explore your home network. With very limited searching on Google, Nessus will lead you to tons of different hacking tools and a wide variety of software, so dig in and learn as much as you can.
Advertisement
SecTools.Org: Top 125 Network Security Tools
For more than a decade, the NmapProject has been cataloguing the network security community'sfavorite tools. In 2011 this site became much more dynamic, offeringratings, reviews, searching, sorting, and a new tool suggestion form.This site allows open source and commercial tools on any platform,except those tools that we maintain (such as the Nmap Security Scanner, Ncat network connector, and Nping packet manipulator).
We're very impressed by the collective smarts of the security community and we highly recommend reading the whole list and investigating any tools you are unfamiliar with. Click any tool name for more details on that particular application, including the chance to read (and write) reviews. Many site elements are explained by tool tips if you hover your mouse over them. Enjoy!
11 tools
(17)★★★Nessus (#3, 2)
Nessus is one of the most popular and capable vulnerability scanners, particularly for UNIX systems. It was initially free and open source, but they closed the source code in 2005 and removed the free 'Registered Feed' version in 2008. It now costs $2,190 per year, which still beats many of its competitors. A free “Nessus Home” version is also available, though it is limited and only licensed for home network use.
Nessus is constantly updated, with more than 70,000 plugins. Key features include remote and local (authenticated) security checks, a client/server architecture with a web-based interface, and an embedded scripting language for writing your own plugins or understanding the existing ones. Read 24 reviews.
Latest release: version 6.3.3 on March 16, 2015 (4 years, 5 months ago).
(30)★★★★OpenVAS (#19, new!)
OpenVAS is a vulnerability scanner that was forked from the last free version of Nessus after that tool went proprietary in 2005. OpenVAS plugins are still written in the Nessus NASL language. The project seemed dead for a while, but development has restarted. Read 36 reviews.
Latest release: version 8.0 on April 2, 2015 (4 years, 5 months ago).
(10)★★★★½Core Impact (#29, 15)
Core Impact isn't cheap (be prepared to spend at least $30,000), but it is widely considered to be the most powerful exploitation tool available. It sports a large, regularly updated database of professional exploits, and can do neat tricks like exploiting one machine and then establishing an encrypted tunnel through that machine to reach and exploit other boxes. Other good options include Metasploit and Canvas. Read 15 reviews.
Latest release: version 12 on Aug. 8, 2011 (8 years ago).
(14)★★½Nexpose (#36, new!)
Rapid7 Nexpose is a vulnerability scanner which aims to support the entire vulnerability management lifecycle, including discovery, detection, verification, risk classification, impact analysis, reporting and mitigation. It integrates with Rapid7's Metasploit for vulnerability exploitation. It is sold as standalone software, an appliance, virtual machine, or as a managed service or private cloud deployment. User interaction is through a web browser. There is a free but limited community edition as well as commercial versions which start at $2,000 per user per year. Read 16 reviews.
Nessus Vulnerability Scanner
(6)★★★½GFI LanGuard (#40, 20)
GFI LanGuard is a network security and vulnerability scanner designed to help with patch management, network and software audits, and vulnerability assessments. The price is based on the number of IP addresses you wish to scan. A free trial version (up to 5 IP addresses) is available. Read 6 reviews.
Latest release: version 2011 on May 19, 2001 (18 years, 3 months ago).
(4)★★★★QualysGuard (#42, 31)
QualysGuard is a popular SaaS (software as a service) vulnerability management offering. It's web-based UI offers network discovery and mapping, asset prioritization, vulnerability assessment reporting and remediation tracking according to business risk. Internal scans are handled by Qualys appliances which communicate back to the cloud-based system. Read 5 reviews.
Latest release: version 6.18 on Feb. 25, 2011 (8 years, 6 months ago).
(3)★★★MBSA (#46, 54)
Microsoft Baseline Security Analyzer (MBSA) is an easy-to-use tool designed for the IT professional that helps small and medium-sized businesses determine their security state in accordance with Microsoft security recommendations and offers specific remediation guidance. Built on the Windows Update Agent and Microsoft Update infrastructure, MBSA ensures consistency with other Microsoft management products including Microsoft Update (MU), Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), Systems Management Server (SMS) and Microsoft Operations Manager (MOM). Apparently MBSA on average scans over 3 million computers each week. Read 3 reviews.
Latest release: version 2.3 on Nov. 12, 2013 (5 years, 9 months ago).
(1)★★★Retina (#54, 29)
Like Nessus, Retina's function is to scan all the hosts on a network and report on any vulnerabilities found. It was written by eEye, who are well known for their security research. Read 2 reviews.
(6)★★★★½Secunia PSI (#68, new!)
Secunia PSI (Personal Software Inspector) is a free security tool designed to detect vulnerable and out-dated programs and plug-ins that expose your PC to attacks. Attacks exploiting vulnerable programs and plug-ins are rarely blocked by traditional anti-virus programs. Secunia PSI checks only the machine it is running on, while its commercial sibling Secunia CSI (Corporate Software Inspector) scans multiple machines on a network. Read 6 reviews.
Nessus Vulnerability Scanner Latest Ver…
Latest release: version 2.0 on Jan. 10, 2011 (8 years, 7 months ago).
(3)★★★★½Nipper (#81, new!)
Nipper (short for Network Infrastructure Parser, previously known as CiscoParse) audits the security of network devices such as switches, routers, and firewalls. It works by parsing and analyzing device configuration file which the Nipper user must supply. This was an open source tool until its developer (Titania) released a commercial version and tried to hide their old GPL releases (including the GPLv2 version 0.10 source tarball). Read 3 reviews.
Latest release: version 1.3.
(4)★★★★½SAINT (#110, 19)
SAINT is a commercial vulnerability assessment tool. Like Nessus, it used to be free and open source but is now a commercial product. Unlike Nexpose, and QualysGuard, SAINT runs on Linux and Mac OS X. In fact, SAINT is one of the few scanner vendors that don't support (run on) Windows at all. Read 9 reviews.
Nessus Security Scanner
Latest release: version 7.13 on May 18, 2012 (7 years, 3 months ago).
11 tools

Comments are closed.